
Google Tag Manager Cookies
Google Tag Manager and Cookies: How to Comply? Insira o seu email para receber gratuitamente as atualizações do blog 13 min read Google Tag Manager

Google Tag Manager (GTM) is an awesome tool for webmasters and marketers. It allows you to safely deploy JavaScript snippets and other tags on your website and change the implementation logic at any time – all without having to touch any code. Moreover, it simplifies the management of tracking codes, making updates faster and reducing the risk of errors. However, with it comes scripts that may use third-party cookies on your visitors’ browsers, therefore, raising privacy concerns. But don’t worry, you can still use GTM without meddling with users’ privacy. In this article, we will see how Google Tag Manager uses cookies and what you can do to comply with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA for cookies.
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a tag management system that allows you to effortlessly manage tags and trackers on your website without having to modify the code directly.
As you probably know, websites have many different types of code running on them. Sometimes that code can be used to track how visitors interact with the site—for example, by recording page views and clicks. GTM helps with this process by allowing you to add and manage these kinds of tags from a single dashboard.
You can add new tags or remove old ones, and then activate them on any site or app. For instance, if you launch a new marketing campaign, you can easily deploy related tracking tags without developer assistance. You can also see which tags are firing on any given page and use its tracking feature to automatically add data points when certain actions occur on your site.
In short, Google Tag Manager lets you:
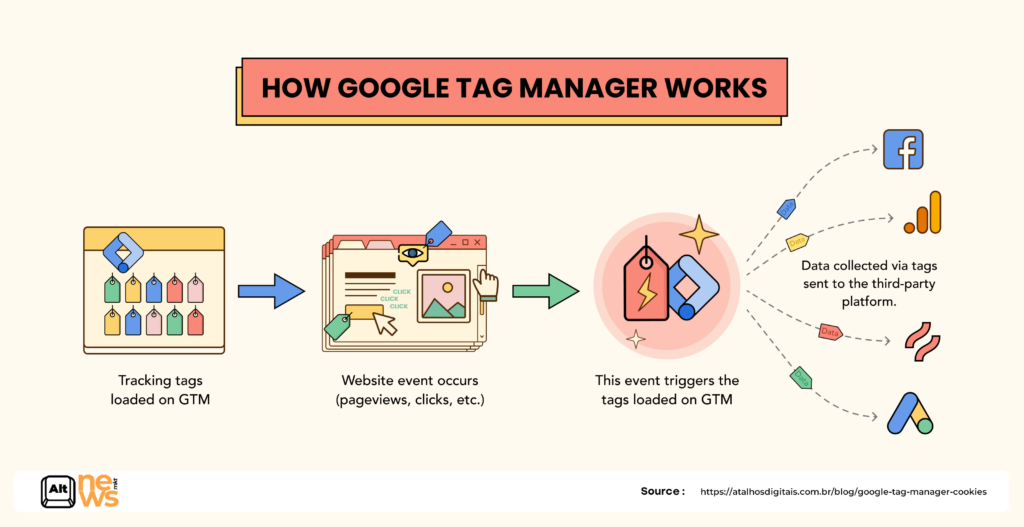
In addition, Google Tag Manager provides flexibility to collect a wide range of user interactions.
You can use Google Tag Manager to:
No, Google Tag Manager does not use cookies, by default. It enables tags for third-party scripts that may place cookies on the user’s device. GTM can read the value of first-party cookies set by your website but does not do anything with third-party cookies.
However, it’s important to note that certain situations may lead to cookie usage. Although Google Tag Manager does not set any cookies, there is one case where they do. If you enable GTM’s Preview and Debug mode, it sets a few first-party cookies on the site being previewed. These cookies are necessary for the Preview mode to work—that is, to display what is happening on your website and which tags are firing. Only site admins or users who have enabled the preview and debug mode will receive these cookies; when you exit Preview and Debug mode, GTM deletes these cookies from your device.
Google Tag Manager is GDPR compliant and allows you to use tags across multiple domains with a single installation. Furthermore, it enhances transparency by giving you full control over the data being collected. It also gives you full control over the data that is being sent to your website, allowing you to have complete transparency over what data is being collected.
It may collect some aggregated data about tag firing to help monitor, provide diagnostics, and improve the quality of its systems. However, this data does not include any personally identifiable information. Other than HTTP request logs that expire in 14 days, and other non-personal diagnostics data, GTM does not collect, store or share any PII about visitors to its users. Neither does it use tracking technologies like cookies.
However, suppose you want to use Google Analytics or other tools on your website via GTM. You need to update your privacy policy accordingly and get consent if these tools collect the personal data of the visitors.
The Tag Manager includes several features that help to manage how tags behave in response to user consent states. Google Consent Mode lets you control how tags behave, including which ones fire on a page and which don’t, depending on whether the user has granted consent for your site.
To ensure legal compliance, understanding and configuring consent triggers is essential. The Consent Initialization trigger in GTM makes sure that all consent settings are executed before tags fire in response to any other triggers. This trigger can be used in conjunction with a third-party provider that integrates with Tag Manager’s consent management capabilities. Each web container includes a Consent Initialization – All Pages trigger by default, which you can select to fire any tags that require it.
Expert tip:
To sum up, following these steps will help you align with privacy regulations effectively. If you use Google Tag Manager on your website to deploy tags that use cookies, you can use this checklist to comply with privacy laws:
Google Tag Manager does not set any cookies on its own. The only time a cookie is set is when you use preview and debug mode, which just gives you a view of what tags are firing on each page. If you’re using third-party tags, they may set cookies on user devices if they have been configured to do so.
If you use Google Tag Manager to manage third-party tags, code snippets, or tracking pixels on your website, those tags may set third-party cookies. If this is the case, then you may need cookie consent to comply with GDPR.
Google Tag Manager is not a first-party cookie. First-party cookies are those set by the same domain as the website in which they are being served, while third-party cookies are set by sites other than the one you’re currently on. Google Tag Manager does not set any cookies at all. The only exception is when you activate its Preview & Debug mode, which sets non-tracking cookies that are essential for the mode to work, and this mode is only visible to the GTM account admins.
Yes, Google Analytics can track cookies.
Google Analytics is a web analysis tool that allows website owners to monitor how people use their sites. It uses cookies to track users as they move from page to page on a site.
The Analytics cookie records information about users’ devices, such as their operating system, IP address, location, and the date and time of their visit. It generates reports on pageviews, session durations, and bounce rates to help you understand how engaging your web pages are. Google Analytics also includes information about the page they visited on your site and what search terms they used when arriving at your site through an organic search result or referral link from another site.
This is why GDPR compliance for Google Analytics is important.

Cesar Augusto – AKA Maxxie
Founder of altNEWS, a specialist in advanced tracking strategies, consent management, and marketing automation. He helps brands navigate the evolving landscape of data privacy and build reliable tracking architectures with tools like Google Tag Manager and CRM integrations. Off the clock, you’ll find him exploring new tech solutions or diving into books about data-driven marketing and AI.
Compratilhar:

Google Tag Manager and Cookies: How to Comply? Insira o seu email para receber gratuitamente as atualizações do blog 13 min read Google Tag Manager
tudo que você precisa saber pra começar seu dia bem e informado.
Os melhores insights sobre marketing digital, vendas, experiência do cliente, desenvolvimento web e transformação digital.
Este site utiliza cookies para garantir que você tenha a melhor experiência em nosso site.